Quote from: Dr. MD MD on February 13, 2023, 07:12:59 PMShit, did you even grauate high school?
Da grauate
This section allows you to view all posts made by this member. Note that you can only see posts made in areas you currently have access to.
Show posts MenuQuote from: Dr. MD MD on February 13, 2023, 07:12:59 PMShit, did you even grauate high school?
Quote from: Dr. MD MD on February 13, 2023, 07:03:23 PMHow do I know you're not lying now?!
Zero cred. 🙄
Quote from: Dr. MD MD on February 13, 2023, 06:51:39 PMSays the guy who rammed another car on the freeway. 🙄
Liberals excel only in projection of their shadow.
Quote from: Dr. MD MD on February 13, 2023, 06:35:02 PMOh hey, here's someone who voted for Biden. You needn't look any further for someone trying to run government through a thoroughly corrupt relationship with big business. You must be happy with all the Bidenflation and environmental degradation currently going on...not to mention the possibility of nuclear war with Russia, right? Hey, what do you think the social credit score of a violent schizophrenic would be? Yeah, me too.
Quote from: Dr. MD MD on February 19, 2021, 01:27:36 PM
You’re also schizophrenic and though Trump was the devil. Reeeeeeeeeeeee!!!!!
Quote from: Jackstar on February 15, 2021, 02:33:00 PM
Congratulations on your release, Stellar, always a plus to get that stuff out the door
I'm not gonna lie, though, I'm probably gonna not read it
Have you read Atlas Shrugged?


Quote“Turbulence action in these flows is similar to what happens when we add cream to coffee. Left alone, the cream takes a long time to mix with the coffee,†said Poludnenko, associate adjunct professor of aerospace engineering in the Department of Engineering and associate professor of mechanical engineering at the University of Connecticut. “But if we stir it with a spoon, we can cause turbulence; so, the motion of the spoon forces the cream and coffee to move faster, greatly accelerating their mixing.â€
To investigate if turbulence could be a reason why volatile gases detonate, the research team designed an experimental setup consisting of a 1.5 meter-long channel with a spark plug installed on one end. Along the length of the chamber the researchers positioned perforated plates at different carefully chosen locations. The plates were designed to promote turbulence in a flammable gas mixture. After igniting the gas, researchers measured the speed of the resulting flame, along with the pressure generated by it, at different locations along the chamber.
Poludnenko and his team observed that the experimentally-induced turbulence within the chamber caused the flame to become unstable, accelerating rapidly and creating shock waves that traveled much faster than the speed of sound. As their theory predicted, these shock waves grew in strength and sped up the rate of burning even more, eventually causing a detonation.
Since their theory described gas detonations well, the researchers next investigated if the same theory could also explain stellar explosions, that is, the detonation of material undergoing nuclear fusion inside white dwarf stars. Upon simulating the turbulent conditions in the blistering core of these stars, Poludnenko and his team found that their theory predicted that much like the events leading up to gas explosions, turbulence can also cause supersonic shockwaves within the star. These waves force the star to chew through its nuclear fuel vigorously, triggering a massive detonation that ultimately blows up the star within a few seconds, producing an explosion capable of outshining the entire galaxy.
Poludnenko noted that while their findings have numerous applications in cosmology and astrophysics, their work also has important applications on Earth as well."
https://today.tamu.edu/2020/01/29/why-some-stars-end-life-in-a-bang/

Quote from: Dr. MD MD on February 07, 2021, 12:33:18 PM
Quote from: ACE of CLUBS on February 06, 2021, 04:54:55 PM
Wondering if '2n+7*2n' is correct ?
Quote from: Could this formula actually have more to do with what below with omega and lambda combined?
½ã ©Øç “×
ΩΛ (Omega sub Lambda)
Instead of the cosmological constant itself, cosmologists often refer to the ratio between the energy density due to the cosmological constant and the critical density of the universe, the tipping point for a sufficient density to stop the universe from expanding forever. This ratio is usually denoted ΩΛ, and is estimated to be 0.6889±0.0056, according to results published by the Planck Collaboration in 2018.[13]
QuoteUniverse may be on the brink of collapse (on the cosmological timescale)
by Lisa Zyga , Phys.org
This is the \"South Pillar\" region of the star-forming region called the Carina Nebula. Like cracking open a watermelon and finding its seeds, the infrared telescope \"busted open\" this murky cloud to reveal star embryos tucked inside finger-like pillars of thick dust. Credit: NASA
(Phys.org)â€"Physicists have proposed a mechanism for \"cosmological collapse\" that predicts that the universe will soon stop expanding and collapse in on itself, obliterating all matter as we know it. Their calculations suggest that the collapse is \"imminent\"â€"on the order of a few tens of billions of years or soâ€"which may not keep most people up at night, but for the physicists it's still much too soon.
In a paper published in Physical Review Letters, physicists Nemanja Kaloper at the University of California, Davis; and Antonio Padilla at the University of Nottingham have proposed the cosmological collapse mechanism and analyzed its implications, which include an explanation of dark energy.
\"The fact that we are seeing dark energy now could be taken as an indication of impending doom, and we are trying to look at the data to put some figures on the end date,\" Padilla told Phys.org. \"Early indications suggest the collapse will kick in in a few tens of billions of years, but we have yet to properly verify this.\"
The main point of the paper is not so much when exactly the universe will end, but that the mechanism may help resolve some of the unanswered questions in physics. In particular, why is the universe expanding at an accelerating rate, and what is the dark energy causing this acceleration? These questions are related to the cosmological constant problem, which is that the predicted vacuum energy density of the universe causing the expansion is much larger than what is observed.
\"I think we have opened up a brand new approach to what some have described as 'the mother of all physics problems,' namely the cosmological constant problem,\" Padilla said. \"It's way too early to say if it will stand the test of time, but so far it has stood up to scrutiny, and it does seem to address the issue of vacuum energy contributions from the standard model, and how they gravitate.\"
The collapse mechanism builds on the physicists' previous research on vacuum energy sequestering, which they proposed to address the cosmological constant problem. The dynamics of vacuum energy sequestering predict that the universe will collapse, but don't provide a specific mechanism for how collapse will occur.
According to the new mechanism, the universe originated under a set of specific initial conditions so that it naturally evolved to its present state of acceleration and will continue on a path toward collapse. In this scenario, once the collapse trigger begins to dominate, it does so in a period of \"slow roll\" that brings about the accelerated expansion we see today. Eventually the universe will stop expanding and reach a turnaround point at which it begins to shrink, culminating in a \"big crunch.\"
Currently, we are in the period of accelerated expansion, and we know that the universe is approximately 13.8 billion years old. So in order for the new mechanism to work, the period of accelerated expansion must last until at least this time (needless to say, a mechanism that predicts that the universe has already collapsed is obviously flawed). The collapse time can be delayed by choosing an appropriate slope, which in this case, is a slope that has a very tiny positive valueâ€"about 10-39 in the scientists' equation. The very gradual slope means that the universe evolves very slowly.
Importantly, the scientists did not choose a slope just to fit the observed expansion and support their mechanism. Instead, they explain that the slope is \"technically natural,\" and takes on this value due to a symmetry in the theory.
As the physicists explain, the naturalness of the mechanism makes it one of the first ever models that predicts acceleration without any direct fine-tuning. In the mechanism, the slope alone controls the universe's evolution, including the scale of the accelerated expansion.
\"The 'technically natural' size of the slope controls when the collapse trigger begins to dominate, but was it guaranteed to give us slow roll and therefore the accelerated expansion?\" Padilla said. \"Naively one might have expected to have to fine-tune some initial conditions to guarantee this, but remarkably that is not the case. The dynamics of vacuum energy sequestering guarantee the slow roll.\"
The idea is still in its early stages, and the physicists hope to build on it much more in the future.
\"There is much to do,\" Padilla said. \"Right now we are working on a way to describe our theory in a way that is manifestly local, which will make it more conventional, and more obviously in keeping with some of the key principles behind quantum theory (namely, linear superposition). We would also like to devise more tests of the idea, both cosmological and astrophysical.
\"Over the longer term, we would like to understand how our theory could emerge from a more fundamental theory, such as string theory. It is also important to ask what happens when we consider vacuum energy corrections from quantum gravity.\"
If there was ever a justification that more work is needed, it may be in the paper's conclusion:
\"The present epoch of acceleration may be evidence of impending doom. . . A detailed analysis to better quantify these predictions is certainly warranted.\""]
https://astronomy.com/magazine/news/2021/02/the-beginning-to-the-end-of-the-universe-a-cold-lonely-death
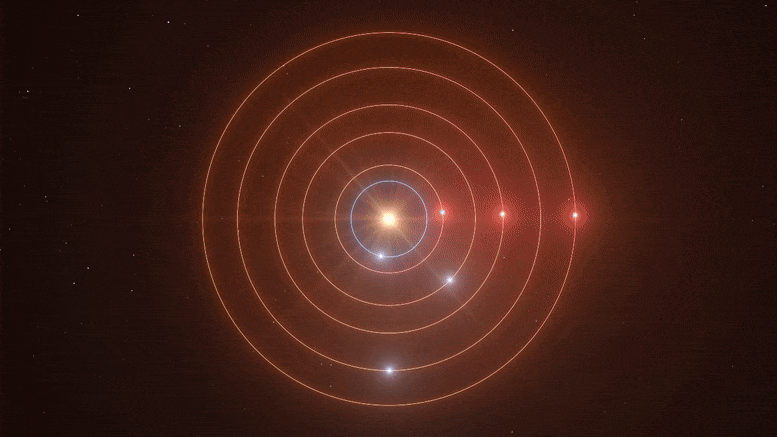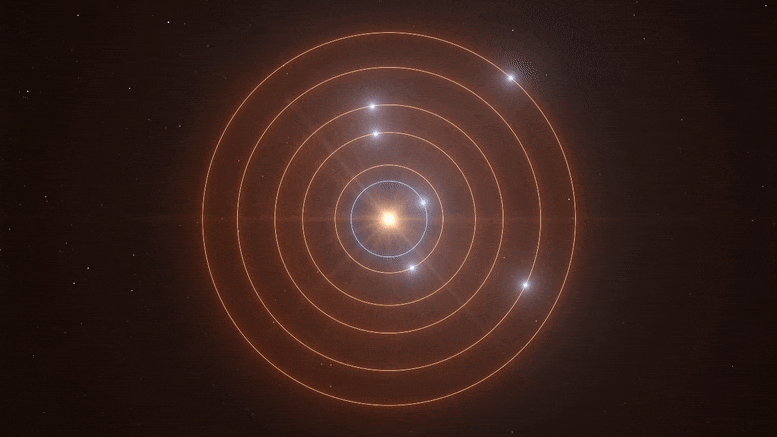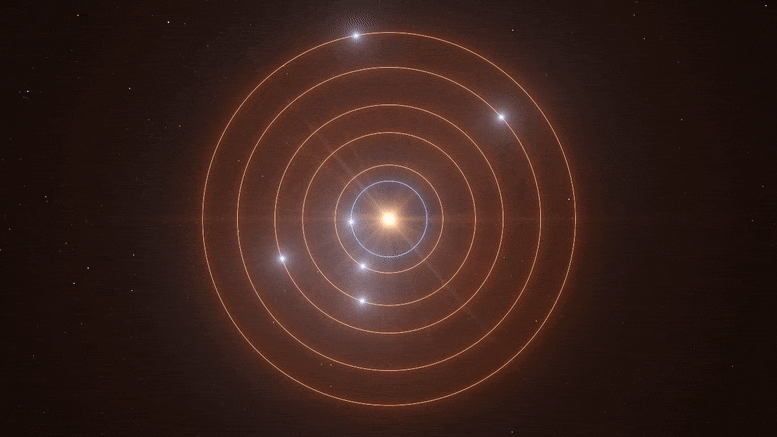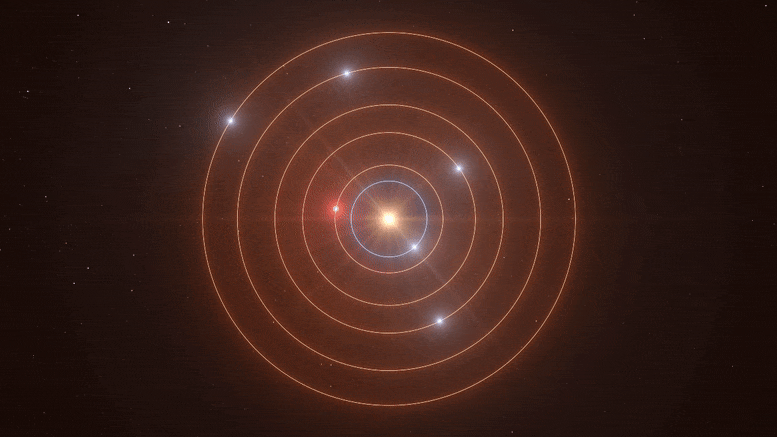
Quote from: Jackstar on February 05, 2021, 08:21:12 PM
Seriously, do we have room in the budget for some bobbleheads? I'm thinking Christmas '22. Somebody: write that down, any colour book will do.
Quote from: pate on February 05, 2021, 05:56:48 PM
@Stellar
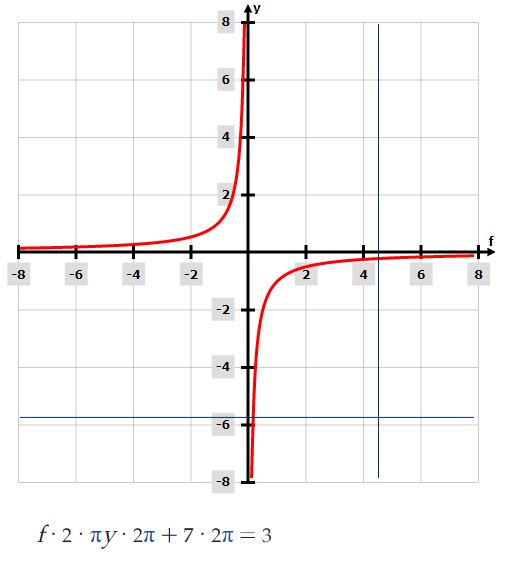
This is a graph of the Circular Function csc(x):
This is a graph of the Circular Function sec(x):
I think the graph of sec(x) and your graph of f(2*πy*2π+7*2π)=3 display some similarities, perhaps the decimal portion of the Hougeland Constant is at work here for the offset?
Again, I am;
Nautical Shore
-p
Quote from: AZZERAE on February 05, 2021, 05:17:35 AM
Oh yeah? Wat do you make of DCLXVI, smartypants?!
Quote from: ACE of CLUBS on February 05, 2021, 04:26:05 PM
Was going to start a new re-cycle program. Guess it's pointless to do so now . . .
 .
.

Quote from: The Earth’s rotation can change slightly because of a lot of factors. The pressure, seismic activity and the general motions of our planet’s inner molten core is a big factor, and it may even rotate just a bit faster than the planet as a whole.
https://www.forbes.com/sites/jamiecartereurope/2021/01/15/do-we-need-a-drop-second-the-worrying-reason-why-earth-may-be-speeding-up-after-decades-of-slowing-down/?sh=4e5375a82204
Quote from: Earth's magnetic field is WEAKENING between Africa and South America, causing satellites and spacecraft to malfunction
The Earth's magnetic field is weakening between Africa and South America
Called the South Atlantic Anomaly, it formed a weakened center in just 5 years
Scientists speculate that this is a sign the Earth is heading to a pole reversal
https://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article-8345553/Earths-magnetic-field-WEAKENING-Africa-South-America-malfunctioning-satellites.html
Quote from: The observations showed that gas was coming out of the comet that contained unusually high amounts of carbon monoxide. There was more of the chemical than had been found in any comet near the sun, and may have been 26 times higher than the average solar system comet.
Watch more
Comet visiting our solar system is 'like nothing seen before'
Comet visiting our solar system is 'like nothing seen before'
Usually, in comets found in our solar system, water is the most abundant molecule in the \"coma\" or gas cloud that surrounds them. But 2I/Borisov had as much as 1.7 times as much carbon monoxide as it did water, the scientists report.
https://www.independent.co.uk/life-style/gadgets-and-tech/news/comet-interstellar-borisov-oumuamua-object-space-nasa-alma-a9474676.html
 . I found another math formula and it comes with a graph which mirrors one straight out of a collapsing universe pdf. By comparing the graphs below one that I found in the message and the one in the 2020 paper of a Collapsing universe it would appear that I'm right. The Universe is currently imploding and if you are sensitive enough you can feel it. Sadly lets get started.
. I found another math formula and it comes with a graph which mirrors one straight out of a collapsing universe pdf. By comparing the graphs below one that I found in the message and the one in the 2020 paper of a Collapsing universe it would appear that I'm right. The Universe is currently imploding and if you are sensitive enough you can feel it. Sadly lets get started.Quote from: Luke 21:25-26
New International Version
25 “There will be signs in the sun, moon and stars. On the earth, nations will be in anguish and perplexity at the roaring and tossing of the sea. 26 People will faint from terror, apprehensive of what is coming on the world, for the heavenly bodies will be shaken.


Quote from: ACE of CLUBS on February 04, 2021, 07:02:18 PM
Would you send me an e-mail the day before all this happens? I've got bottled water, pork & beans, and extra toilet paper in the basement. Just ride it out . . . .
Quote from: Asuka Langley on February 03, 2021, 10:20:09 PM
Psssst hey kid, you want to buy some apple flavored horse wormer paste?